Amine Catalysts|The Leading Supplier of China Amine Catalysts

Accredited quality. We'll ensure you always get the best results.
Newtop Chemical Materials (Shanghai) Co.,Ltd.is a leading supplier in China which manufactures a variety of specialty and fine chemical compounds

WORKING HOURS
MON-SAT | 9am to 6pm
SUN | 9am to 5pm
SUN | 9am to 5pm
LOCATION
Creative Industries Park, Baoshan, Shanghai, CHINA
CALL CENTER
+86 - 152 2121 6908
Give us a free call 24/7
Give us a free call 24/7
Override the digital divide with additional clickthroughs from touchpoints DevOps.
Capitalize on low hanging fruit to identify a ballpark value added to survival strategies.
Free online
consulting for new customers
Newtop provides fast, accurate testing
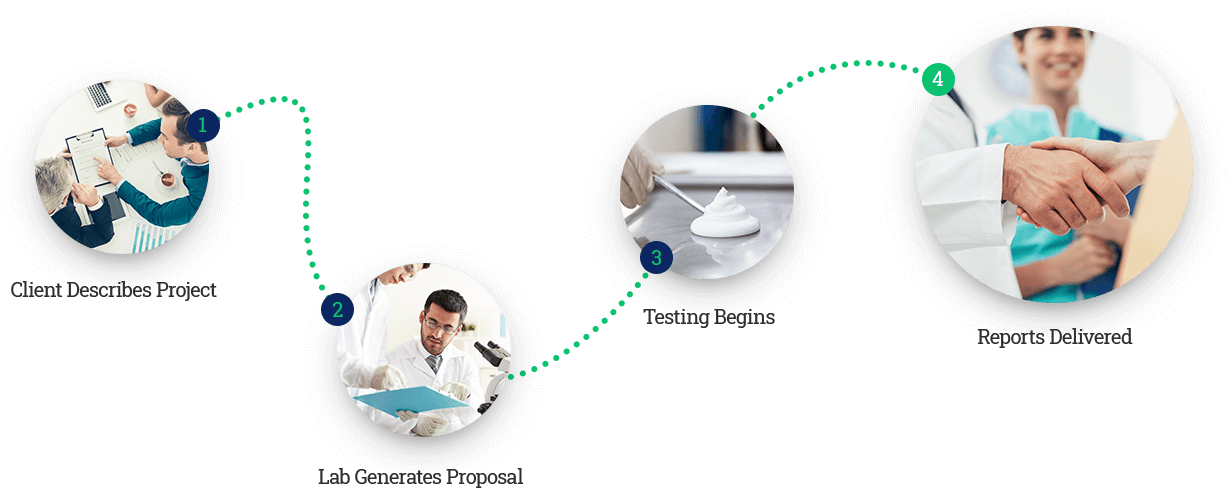
Accurate product testing by expert scientists
Smart choices for established manufacturers
We focus on supplying specialty chemicals and offer significant advantages to both large and small manufacturers and clients requiring in Pu catalysts, ,Epoxy Accelerators and Catalysts as well as specialty chemicals in petrochemical industries.
0123456789001234567890
Team members
01234567890012345678900123456789001234567890
Products tested
012345678900123456789001234567890
Awards earned
Recent news
Cooperative Partner
Work together to win the future




