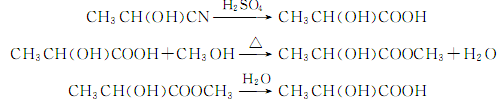Structural formula
| Business number | 0139 |
|---|---|
| Molecular formula | C3H6O3 |
| Molecular weight | 90.08 |
| label |
DL-2-hydroxypropionic acid, Propanol acid, alpha-hydroxypropionic acid, DL-2-Hydroxypropanoic acid, Racemic lactic acid, a-Hydroxypropionic acid, sour agent, fungicides, preservative, antifungal agent, mordant, deliming agent, acidic solvent |
Numbering system
CAS number:50-21-5
MDL number:MFCD00004520
EINECS number:200-018-0
RTECS number:OD2800000
BRN number:1209341
PubChem number:24901202
Physical property data
1. Properties: The pure product is a colorless or slightly yellow viscous liquid with a sour milk smell and strong hygroscopicity.
2. Density (g/mL, 25/4℃): 1.209
3. Melting point (ºC, DL-lactic acid): 17~18
4. Melting point ( ºC, D-, L-lactic acid): 52.8
5. Boiling point (ºC, normal pressure): 122 (2kpa)
6. Refractive index (20ºC): 1.4351
7. Flash point (ºC): >110
8. Specific rotation (º): -0.05 º (c= neat 25 ºC)
9. Heat of combustion (KJ/mol, 25ºC): 1368.3
10. Solubility: Can be mixed with water, ethanol, and glycerin at will, soluble in ether, and insoluble in chloroform, petroleum ether and carbon disulfide.
Toxicological data
1. Skin/eye irritation: rabbit, skin contact, standard Draize test: 5mg? 24H, strong reaction; rabbit, eye contact, standard Draize test: 750ug, strong reaction 2. Acute toxicity: rat oral LD50: 3543mg/ kg; mouse oral LC50: 4875mg/kg; rabbit oral LDLo: 5mg/kg; rabbit skin contact LD50: >2mg/kg; rabbit rectal LD50: 600mg/kg; guinea pig oral LD50: 1810mg/kg; quail Oral LD50: >2250mg/kg3. Mutagenicity: Mutant microorganism detection system: Bacteria – Escherichia coli: 210ppm/3H4. It is of low toxicity and has no accumulation effect, but a large dose (1.5g/kg) is given to rats orally every day. ) lactic acid, causing weight loss, anemia, and increased carbon dioxide levels in the blood. Concentrated lactic acid solution can burn the skin and cause turbidity and gangrene in the cornea. Pay attention to protecting the skin and eyes when using it.
Ecological data
None
Molecular structure data
1. Molar refractive index: 19.00
2. Molar volume (cm3/mol): 70.5
3. Isotonic specific volume (90.2K ): 187.4
4. Surface tension (dyne/cm): 49.7
5. Dielectric constant (F/m):
6. Dipole Distance (D):
7, Polarizability (10-24cm3): 7.53
Compute chemical data
1. Reference value for hydrophobic parameter calculation (XlogP): None
2. Number of hydrogen bond donors: 2
3. Number of hydrogen bond acceptors: 3
4. Number of rotatable chemical bonds: 1
5. Number of tautomers: none
6. Topological molecule polar surface area 57.5
7. Number of heavy atoms: 6
8. Surface charge: 0
9. Complexity: 59.1
10. Number of isotope atoms: 0
11. Determine the number of atomic stereocenters: 0
12. Uncertain number of atomic stereocenters: 1
13. Determine the number of chemical bond stereocenters: 0
14. Number of uncertain chemical bond stereocenters: 0
15. Number of covalent bond units: 1
Properties and stability
1. Chemical properties: Lactic acid has hydroxyl and carbonyl groups, and when heated, it produces linear polyester like lactide. The initial esterification product is lactoyl lactic acid, and as the concentration increases, polylactic acid is formed.
Most of them produce linear polymers, and some produce lactide.
Lactic acid decomposes into acetaldehyde, carbon monoxide and water during dry distillation. Lactic acid monoester decomposes into acetaldehyde and carbon monoxide during dry distillation, and becomes a polymer of lactic acid in the presence of a catalyst.
However, lactic acid diesters produce acrylate and acetic acid during dry distillation.
Lactic acid has the properties of a general organic acid, and its salts are soluble in water. Can form esters with most alcohols. To inhibit the formation of lactic acid polymers, excess alcohol can be used. The hydroxyl group in the lactic acid molecule can also react with organic acids, acid anhydrides, acid chlorides, etc. to form esters. When heated with dilute sulfuric acid, it decomposes into formic acid and acetaldehyde.
2. Pure and non-toxic. Its salts are non-toxic as long as they are not heavy metal salts. Oral LD503730mg/kg in rats.
3. Exist in tobacco leaves and smoke.
4. Naturally found in cooked beef, cocoa, and wheat bread.
5. It also exists in muscles, especially after intense muscle activity, the content of lactic acid increases, so the muscles feel swollen.
Storage method
1.20kg glass bottles are packed in wooden boxes or sealed in plastic barrels. Store in a clean and dry place.
2. The medicinal small package is 500g and the reagent bottle is available. Edible lactic acid is packed in plastic barrels, with a net weight of 25kg per barrel. Pay attention to sealed storage. Store and transport according to general chemical regulations.
Synthesis method
1. Use starchy raw materials, molasses, starch sugar, etc. as raw materials. After saccharification, use suitable acid lactic acid bacteria or Bacillus to ferment under suitable conditions, neutralize and precipitate with calcium carbonate, and then use dilute sulfuric acid to make it It is converted into lactic acid and then refined to obtain lactic acid finished product.
Starch saccharification ↓ Glucoamylase fermentation ↓ Lactic acid bacteria neutralization Press filtration Concentration Cooling Acidification Decolorization ↓ Activated carbon ↓ Sulfuric acid filtration Vacuum concentration Cation exchange Anion exchange Vacuum concentration Decolorization Suction filtration finished product
Refining method : Lactic acid has strong hygroscopicity. When concentrated, part of the lactic acid becomes anhydride, and it is prone to esterification reaction when heated. Therefore, even if it is distilled under reduced pressure, it is difficult to obtain a pure product. During refining, fractionate under a pressure of 13.3 Pa. The distillate is dissolved in a mixture of equal amounts of diethyl ether and isopropyl ether, and is cooled and crystallized at ice-salt temperature. After filtration, crystallization was repeated twice. Crystallization can also be carried out at dry ice temperatures. The solvent can also be a mixed solvent of equal amounts of benzene and diethyl ether containing 5% petroleum ether (b.p. 60~80℃).
2. There are three methods for industrial production of lactic acid, fermentation, acetaldehyde and acrylonitrile. The most widely used method at present is the fermentation method, which uses starch-containing raw materials sucrose, beet sugar, molasses or grain starch as raw materials, saccharifies and inserts lactic acid bacteria, ferments for 3 to 4 days at pH = 5 and 49°C, and uses calcium carbonate to and, filter while hot to refine calcium lactate. Then acidify with sulfuric acid, filter, and concentrate the filtrate, decolorize, and remove impurities to obtain the product.
3 Synthesis method
Chemical synthesis includes acetaldehyde method and acrylonitrile method, and the lactic acid produced is DL. Lactic acid.
(1) The acetaldehyde method uses acetaldehyde and hydrocyanic acid as raw materials to react to produce lactonitrile, which is hydrolyzed to obtain crude lactic acid. The crude lactic acid is esterified with ethanol and then hydrolyzed to obtain lactic acid:
Put acetaldehyde and cold The hydrocyanic acid is continuously fed into the reactor to generate lactonitrile, which is then pumped into the hydrolysis kettle, and water and sulfuric acid are added to catalyze the hydrolysis to obtain lactic acid; ethanol is added for esterification and the ethyl lactate is distilled out; and finally sent to the concentration tank for heating. Decomposed to obtain refined lactic acid.

(2) Acrylonitrile method: obtained by hydrolysis of acrylonitrile Crude lactic acid is then esterified with methanol and then hydrolyzed to obtain lactic acid:
Acrylonitrile is sent to the reactor and hydrolyzed under the catalysis of sulfuric acid to form lactic acid.A mixture of �� and ammonium bisulfate. The mixture enters the esterification reactor and is esterified with methanol. After ammonium bisulfate is separated, the crude ester is sent to the distillation tower, and the refined ester is obtained at the bottom of the tower. The refined ester is then sent to the distillation tower and decomposed by heating to obtain dilute lactic acid. Finally, the product is obtained through vacuum concentration.
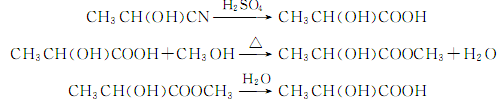
4. Tobacco: BU, 26 . In the food industry, it is prepared by the fermentation of glucose, starch and milk; acetaldehyde reacts with hydrocyanic acid to generate cyanoethanol, which is then hydrolyzed to produce crude lactic acid. Acetolactic acid is converted into ethyl lactate, and then hydrolyzed into pure lactic acid.
Purpose
1. It can be used as a sour agent with preservative effect in the food industry. It can be used in alkyd resins in the chemical industry to help improve quality. It can also be used to prepare food emulsifiers. In the printing and dyeing industry, it can be used as a phenylamine anti-dyeing agent to prepare printing dye slurry, etc. In the leather industry, it can be used for leather deashing, which can shorten tanning time and improve leather quality. It can also be used to produce biodegradable polymer materials such as polylactic acid. Used as a solvent for non-water-soluble dyes such as phenazine blue and alcohol-soluble sky blue. In the food industry, it is used as a general sour agent, bactericide, preservative, antifungal agent, etc. Used as mordant and solvent in dyeing industry. Used as deliming agent in leather industry.
2.Mainly used as a conditioner and emollient for skin or hair, and an acidifier to adjust the pH value. It is used in skin care creams and lotions, in hair care products such as shampoos and conditioners, and in shaving products and detergents.
3.Food sour agent, preservative, preparation of lactate, plasticizer and used in tanning, wool spinning, Printing and dyeing, pharmaceutical and other industries. Used in cosmetics to make acidic creams.
4.Lactic acid is used as a complexing agent for chemical nickel and other metals, and can also be used as an additive for electroplating.
5. Originally obtained from kefir, hence the name lactic acid. Lactic acid is widely distributed in nature. Lactic acid is produced in fermented feed and pickled sauerkraut.
6. Lactic acid is used as a calcium remover in industry, mainly in fruity and dairy flavors. Used in cheese, meat products, and dairy products.
extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/31-10.jpgextended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/polycat-2-catalyst-cas10294-43-5-evonik-germany/extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44380extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44748extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/44245extended-reading:https://www.morpholine.org/soft-foam-amine-catalyst-b16-hard-foam-amine-catalyst-b16/extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/115-3.jpgbr>extended-reading:https://www.bdmaee.net/wp-content/uploads/2022/08/Dibutyl-tin-maleate-CAS78-04-6-tributyl-tin-oxide.pdfextended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/40065extended-reading:https://www.newtopchem.com/archives/40530