On February 7, 2024, the European Commission formally adopted a proposal to reduce the occupational exposure limits (OEL) of lead and diisocyanates with an overwhelming vote, aiming to protect those engaged in building renovation, battery production, and wind power generation. The health and safety of workers in industries such as machine manufacturing and electric vehicle lightweighting. The updated content of the proposal is as follows:
Lead:
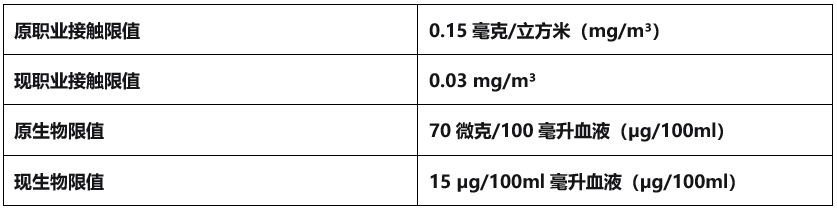
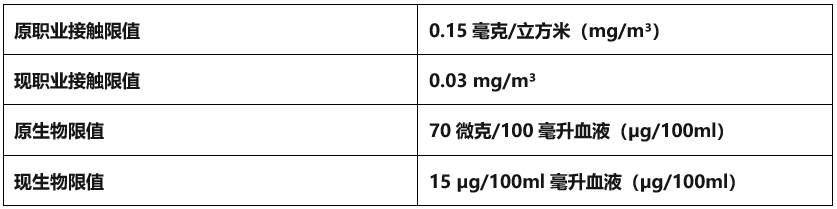
Lead enters the human body mainly through breathing, food and water intake. It is particularly common in some industrial activities, paint with high lead content, and old water pipes. Long-term exposure to high concentrations of lead can lead to high blood pressure, cardiovascular disease, kidney damage and reproductive system problems. In response, the European Commission and Council set occupational exposure limits and biological limits.
Since it takes a certain amount of time to implement risk management measures, and companies need a lot of money to adjust their production processes, it may be difficult to reduce the biological limit of blood lead to 15 micrograms per 100 ml in the short term. Therefore, the transition period given to enterprises is until December 31, 2028, during which the biological limit of blood lead is tentatively set at 30 micrograms per 100 milliliters.
Diisocyanate:
Diisocyanate is widely used in foam plastics, paints, and adhesives in the production of pharmaceuticals and other industrial fields. Long-term exposure may cause asthma, atopic dermatitis, headaches, dizziness and other diseases, and may even cause cancer.
Currently, the EU has not yet established legally binding occupational exposure and short-term exposure limits for diisocyanates. This proposal sets the first limit standard for diisocyanates, setting the occupational exposure limit to 6 μg NCO/m3 per cubic meter (i.e. within 8 hours), and the short-term exposure limit to 12 μg NCO/m3 (i.e. 15 minutes). Inside).
Similar to lead, the proposal provides for a transition period until December 2028 for an occupational exposure limit of 10 micrograms NCO/m3 and a short-term exposure limit of 20 micrograms NCO/m3. March 31st.
The regulations will be published in the Official Journal of the European Union after formal approval by the European Council.
extended reading:
N-Methylmorpholine
4-Formylmorpholine
dimethomorph
3-morpholinopropylamine
4-Acryloylmorpholine
N-Acetylmorpholine
N-Ethylmorpholine
Morpholine
High Quality 3164-85-0 / K-15 Catalyst / Potassium Isooctanoate
High Quality Bismuth Octoate / 67874-71-9 / Bismuth 2-Ethylhexanoate